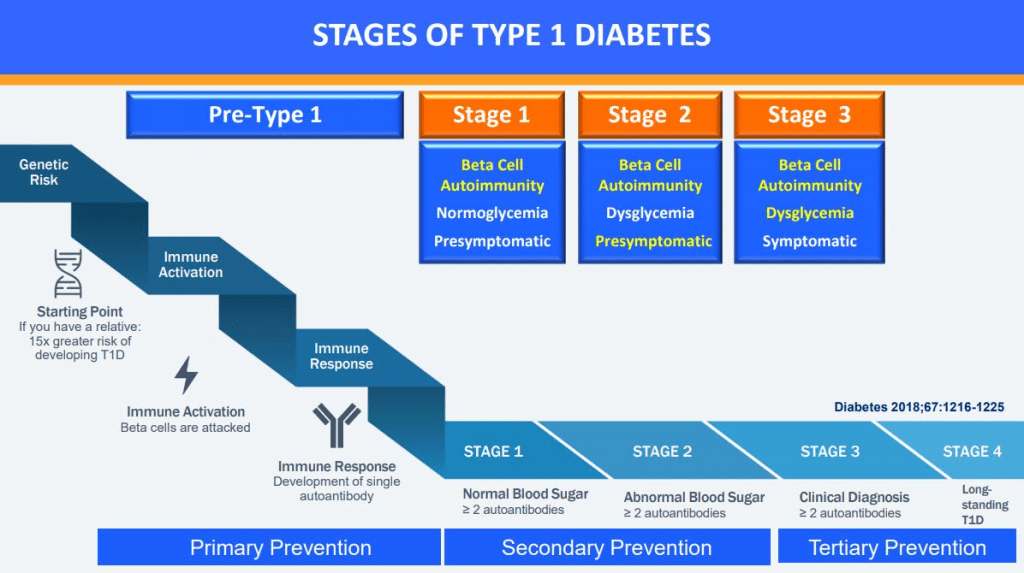
This week, on the 3rd July, 2024, the Australian government released the 23 recommendations resulting from their Inquiry into Diabetes. This blog will review each recommendation and consider its impact on people living with diabetes, and how the Australian government manages diabetes in general. The blog is quite long, so if you want the short version, head on over to the tl;dr section.
Details of the Inquiry
The Inquiry kicked off back in 24 May, 2023 when the Honorable Mark Butler MP called for a committee to investigate and report on diabetes. The Terms of Reference for the inquiry were, according to the committee’s chair, Doctor Mike Freelander, “very broad” with a view to “get as much information as we can so we can get a plan for the future”. Reading the article, the motivation for the inquiry seemed to be the incidence of obesity and type 2 diabetes in Australia and coincided with the release of a study from Deakin University confirming an increase in the rate of type 2 diabetes in Australia.
This was not an inquiry targeted at type 1 diabetes, but at diabetes in general, with obesity and risk factors also being considered. This is reflected directly in the formal Terms of Reference for the inquiry:
“The Committee will investigate:
- The causes of diabetes (type 1, type 2 and gestational) in Australia, including risk factors such as genetics, family history, age, physical inactivity, other medical conditions and medications used;
- New evidence-based advances in the prevention, diagnosis and management of diabetes, in Australia and internationally;
- The broader impacts of diabetes on Australia’s health system and economy;
- Any interrelated health issues between diabetes and obesity in Australia, including the relationship between type 2 and gestational diabetes and obesity, the causes of obesity and the evidence-base in the prevention, diagnosis and management of obesity; and
- The effectiveness of current Australian Government policies and programs to prevent, diagnose and manage diabetes.”
The problem I have with investigating the “interrelated health issues between diabetes and obesity” and “risk factors such as genetics, family history, age, physical inactivity…” is these do not apply to all diabetes types equally, and also apply to other diseases, such as breast cancer. As can also be seen in this last link, risk factors are often conflated with causation. Correlation is not the same as causation and, in the case of diabetes, leads to a lot of unnecessary blame and stigma (there are plenty of skinny type 2s, chubby type 1s, and muggles of both sizes, so broad correlations have limited application at the level of the individual, especially when a proven chain of causality has not been established.)
As it was a public inquiry, submissions and public hearings were part of the process giving a voice, to any interest group who felt the inquiry Terms of Reference related to them, for consideration. So, from the start, there was potential for recommendations which may address broad health issues in the Australian population but not necessarily address prevention of diabetes, treatment of diabetes, or improvements for those living with diabetes. As you will see below, this lack of focus in the Terms of Reference led to a lack of focus in the Recommendations with some having tenuous links to diabetes, at best.
Let us review the recommendations and consider their implications.
The 23 Recommendations
Recommendation 1: The Committee recommends that the Australian Government undertakes a comprehensive economic analysis of the direct and indirect cost of all forms of diabetes mellitus in Australia.
This is an excellent idea. Approval for subsidised medications, equipment, and treatments rely on favourable economic consequences. Approval may require a measure of economic return e.g. spend $1 and return $2 worth of productivity within a specific time period, or an estimation of the cost for ‘Quality-Adjusted Life Years’ (QALYs.) In the case of the NDSS subsidy for CGMs, the cost came in at around $35,000 per QALY, below the unofficial approval threshold of $50,000 per QALY. Subsidies for things like Type 2 CGMs or Type 1 Loops will need to go through a similar exercise. Basically, accurate economic analysis will lower the barriers for smart decisions to be made.
Recommendation 2: The Committee recommends that the National Health and Medical Research Council expedites a review of the Australian Dietary Guidelines, and ensures that the revised guidelines include adequate information for Australians living with diabetes.
Here we see the broader terms of the inquiry coming into play. I do not see a lot coming out of this other than education programmes for ‘guides to healthy eating’. I do not believe information access is the problem. I think we all know we need to move more and eat less, preferably eating food with lower energy density. I can almost guarantee any “adequate information for Australians living with diabetes” will concentrate on type 2 diabetes and its risk factors and largely ignore any other type whose needs are different (people with type 1 are less concerned with glycaemic index/load and more concerned with total carbohydrate count, for example.) The cynic in me has no expectation this level of nuance will be captured in any revisions and expect the guidelines will not go much deeper than “fat bad, protein good, but remember to eat some carbs.”
Recommendation 3: The Committee recommends that the Australian Government implements food labelling reforms targeting added sugar to allow consumers to clearly identify the content of added sugar from front-of-pack labelling. This food labelling initiative should be separate from the information regarding added sugar potentially being included in the Nutrition Information Panel.
This one has little to do with people living with diabetes, whose concerns are carbohydrates in general, rather than just added sugar. I see this adding no value to me personally and see it causing a lot of confusion for people with type 1 diabetes. When bolusing, the need of a person using insulin is for clear carbohydrate labelling. This should not be sacrificed for ‘added sugar’ warnings.
The other concern I have is this recommendation will be seen as ‘proof’ that eating sugar causes diabetes. The causes of diabetes types 1 and 2 are unknown i.e. the reason the immune system starts attacking the pancreas in type 1 is still not understood. Even the proof that sugar causes obesity is limited so, given the Terms of Reference, I think sugar was over-represented in this inquiry.
Recommendation 4: The Committee recommends that the Australian Government implements a levy on sugar-sweetened beverages, such that the price is modelled on international best practice and the anticipated improvement of health outcomes. The levy should be graduated according to the sugar content.
Sugar levies in other countries have shown a decrease in sugar consumption and a slowing of obesity rates in children but that is all the evidence shows so far. While reductions in rates of type 2 diabetes are predicted, using the risk correlations, there has not been enough time to confirm the prediction. I am not against the idea of a sugar tax (my secret hope being it will increase the variety of sugar-free drinks on the supermarket shelves), I am simply uncertain of its place in this inquiry. The hypothesis that sugar consumption leads to weight gain which may lead to an increased rate of obesity which may lead to an increase in the rate of type 2 diabetes seems tenuous to me in its relevance for an inquiry into diabetes of all types.
Recommendation 5: The Committee recommends that the Australian Government considers regulating the marketing and advertising of unhealthy food to children, and that this regulation should:
- Focus on children defined as those aged 16 and under
- Be applied to television, radio, gaming and online
- Use definition of unhealthy food that has been independently developed.
More recommendations relating to general population health with little consideration for diabetes specifically. At least Recommendation 2 threw diabetes in at the end. Again, I am not against lumping in unhealthy food in with cigarettes and alcohol, in terms of advertising, I am simply struggling to link the recommendation to diabetes and the Terms of Reference. My guess is the link is unhealthy food may lead to obesity which increases the risk of type 2 diabetes but I am surprised there were not recommendations raised with a more direct link to diabetes prevention and management. For example, Teplizumab is proven to delay stage 3 type 1 diabetes by literally years so why has it been left out of the recommendations, but an unproven sugar tax included?
Recommendation 6: The Committee recommends that the Australian Government provides its response to the Australian Food Story: Feeding the Nation and Beyond report and considers a dedicated resource within the Department of Health and Aged Care to support access to healthy food to all Australian communities.
For the curious, the referenced report can be found here. The report is focussed on food production and food security but was not about links between food and health. In fact, the word ‘health’ gets mentioned only three times throughout the report’s recommendations. Once in reference to the National Health and Medical Research Council and, of the other two references, the first calls for a National Food Council to advise the government of food matters of which ‘Health and Nutrition’ was one of ten factors to be considered. The second reference called for changes to funding research on ‘food, health and nutrition.’
As we can see, there is a theme here that food, and specifically, sugar is considered the culprit to Australia’s health issues and incidence of diabetes (diabetes type be damned). There is no doubt that access to healthy food is a good thing for Australia in general but, for me, these food recommendations miss the mark for an inquiry on diabetes of all types.
Recommendation 7: The Committee recommends that the Australian Government, in consultation and cooperation with state and territory governments, develops a best practice framework to tackle the problem of obesogenic environments, including through better urban planning and the development of physical activity initiatives and supports efforts to increase access to regular exercise in schools and neighbourhoods as a matter of urgency.
This is a recommendation exclusively considering obesity. The Term of Reference for obesity was “Any interrelated health issues between diabetes and obesity in Australia, including the relationship between type 2 and gestational diabetes and obesity, the causes of obesity and the evidence-base in the prevention, diagnosis and management of obesity.” The recommendation implies that lowering the barriers to physical exercise in urban areas will impact obesity levels. It is a reasonable hypothesis but I could not find a lot of evidence to prove it, similar to the case with sugar leading to obesity and type 2 diabetes. So, again, I question the relevance of this recommendation to this inquiry.
The recommendation is another nice idea for general health improvement but, for tackling how Australia manages diabetes? For me, it seems a poor foundation to build on. Perhaps funding research to work out the causes, rather than acting on the correlations and hoping for the best, would be a better use of money. To mix metaphors, we want to smash the causal chain, not throw stuff at the wall and see what sticks.
Recommendation 8: The Committee recommends that the Australian Government explores the potential for effective national screening programs for all forms of diabetes, particularly Type 2 diabetes.
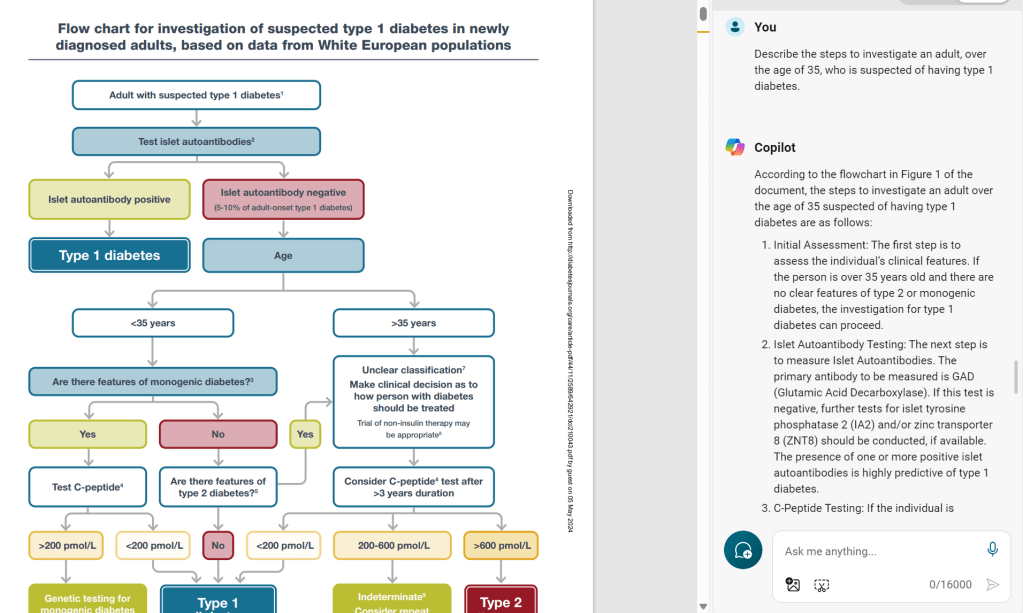
I appreciate I have not been completely glowing in my appraisal of the recommendations so far but this one strikes me as really ill-conceived. Screening for every type of diabetes except type 2 diabetes makes more sense. For type 1, for example, we recently saw the approval for a national screening program in Italy. So why not type 2? Because there is no simple test to definitively diagnose type 2 diabetes. For type 1 we can test for auto-antibodies (which appear years before symptoms) and for MODY we can conduct genetic testing but, for type 2, the test is the symptoms i.e. elevated blood sugars and their effects on the body. There is literally no test we can conduct on a baby to determine if they are going to get type 2 diabetes and even in adults, diagnosis is a series of tests, not some simple screener.
The best we could do would be to implement regular testing of HbA1c which tells us the person may have some form of diabetes but is certainly not definitive for type 2. An elevated HbA1c, in the absence of a diagnosis of diabetes, is referred to as Pre-Diabetes and it is estimated over 1/3 of the US adult population is pre-diabetic. That is a lot of noise to filter out to find the true type 2 diabetics.
The idea of screening for MODY and type 1 diabetes makes sense to me, assuming it is cost effective (see commentary of Recommendation 1). Screening for MODY makes sense to reduce the widespread misdiagnosis and resulting mistreatment, and screening for type 1 makes sense because immune interventions can delay the onset of symptoms for years. It is clear though, screening only makes sense if something is going to be done with a positive test. Unless medical interventions are part of the overall strategy, screening is useless.
Recommendation 9: The Committee recommends that the Australian Government implements a national public health campaign to increase public awareness of the early signs of all forms of diabetes mellitus.
By the early signs for all forms of diabetes, I assume they mean the “Four T’s” which indicate an insufficient amount of insulin in the blood. Certainly, prior to diagnosis, I had enough awareness of two of the T’s (Toilet and Thirst) to know I needed to see a doctor when I was permanently thirsty and peeing every 30 minutes. Given awareness could prevent DKA death in an undiagnosed type 1, I do have some sympathy for this recommendation, assuming it is cost effective.
Recommendation 10: The Committee recommends that the Australian Government funds the development of education-based obesity screening information and resources.
More obesity recommendations which, again, speak to the health of the general population, rather than at diabetes. As with the screening in Recommendation 8, it only makes sense if there is a resulting intervention strategy for those positively identified. While ‘resources’ suggests some level of funded intervention, it is a bit nebulous.
Recommendation 11: The Committee recommends that the Australian Government implements a national public health campaign to increase awareness of the importance of prevention, identification of early signs, and good management of all forms of diabetes mellitus.
This is similar or, at least, related to Recommendation 9 regarding early signs. Prevention is an interesting one. Again, we are predicating our actions off of correlations, given the causes of diabetes in many of its forms (including type 1 and 2) are unknown. If the cause is unknown, how can we prevent it and raise awareness on what is needed to prevent it? As alluded to earlier, the usual suspects for ‘prevention’ equally apply to other diseases as they do to diabetes.
“Good management”, I assume, means eating less and moving more. I doubt this will include, for example, a national public health campaign on the correct use of insulin or on the importance of a well-rounded health care team.
What this is really recommending is a public health campaign to improve the overall health of Australians.
Recommendation 12: The Committee recommends that equitable access to health care for people living with all forms of diabetes be improved through:
- Access to longer appointments with a health care provider subsidised by the MBS
- Access to case conferencing models of health care, especially in rural and remote areas
- Access to telehealth services
- Increase in the number of item numbers for allied health consultation for those with diabetes for diabetes educators and dieticians and other allied health providers
- Access to diabetes educators, including in high-risk outer metropolitan, rural and remote communities.
Finally! A recommendation which actually considers diabetes specifically, rather than being about general population health and issues of sugar consumption, a lack of exercise, and obesity. We are about halfway through the recommendations and, by my reckoning, maybe three of the 12 recommendations are specifically targeted at diabetes, rather than general population health.
Longer appointments are a nice idea if there is something to talk about. I would personally like to see more research and effort being put into structuring the conversations with health care providers so they are more relevant to the person with diabetes (PWD) and deliver real value, rather than being a doctor taking twice as long to tell their client they need to use insulin properly, eat ‘healthier’ carbs, lose weight, and do more exercise. How about a session where the concerns of the PWD are discussed BEFORE the blood results? How about a discussion around the various technologies available and why they may or may not be relevant/desirable to the PWD? How about a discussion of the various medications available which may be of benefit? I am hoping to construct a framework for such a discussion applying corporate motivation theory but this takes time. You can read details of my idea here.
I had to look up “case conferencing” but, from what I can tell, it is health care professional speed dating. Basically, you round up a team of health care professionals (Endo, Dietician, Exercise Physiologist etc.) and have people meet with them as part of a single session. Given the lack of health care professionals in rural areas the organised corralling of them in one spot, and the recommendation for telehealth services make a lot of sense.
Assuming it is done with cultural consideration, I see this having a huge impact in rural aboriginal communities. Aboriginal people are four times more likely to have diabetes/pre-diabetes than their non-indigenous counterparts. Anything that can be done to lower the barriers to health care and education access for these disproportionately affected communities is a good thing.
Then we move on to diabetes educators, a topic of particular interest for me. Firstly, fixing the ‘item numbers’ for allied health professionals is a great idea. A key reason why I do not see my diabetes educator is Medicare and my private health insurance do not recognise the visits. My Diabetes Educator has a Provider Number but, for whatever reason, the visits fall between the cracks. My hope would be that this recommendation would fix that.
Access to diabetes educators (DEs) is a problem in Australia whether it is in urban or rural areas although other HCPs seem to cover the shortfall so that the health of PWDs does not suffer. The online forums constantly buzz with people craving access to a DE but they either do not have one in their area or the DEs are booked out. The pathway to becoming a DE is quite narrow in that you must have a health-related qualification (dietician, nurse etc.) before you can become accredited as a DE.
My personal belief is a person who has lived with diabetes for, say, ten years, could offer tremendous value to someone newly diagnosed but the prospect of studying for three years to obtain a health degree so they can then study to be a DE is a barrier too high for many. A solution might be for a sub-accreditation for non-HCPs where PWDs can assist the newly diagnosed in a structured manner. The pool of available talent would increase and, if managed properly, would not compromise the quality of service given.
Recommendation 13: The Committee recommends that the Australian Government reviews the limits for accessing juvenile mental health and diabetes services, with a view to enabling young people to continue receiving support for longer.
I am unsure which specific programs this relates to, but it sounds like there are specific programs where the recipients ‘age out’, similar to what used to happen with the CGM subsidies when it was limited to people with type 1 diabetes who were 21 years and under. I can see this being particularly important in the case of mental health services where suddenly cutting off the services because of a birthday could be disastrous. This being said, the supply of mental health professionals, such as psychiatrists, is very limited with many having waiting lists stretching for months.
It may also be alluding to the largely useless Insulin Pump Program which subsidises insulin pumps for people with type 1 diabetes under the age of 21. To date, the program has not had a significant impact so broadening the pool of potential recipients would be good.
Recommendation 14: The Committee recommends the Australian Government work with the state and territory governments to develop education tools and resources to support all staff across the health care system to improve understanding of diabetes, its different forms, the early signs and management. The Diabetes in Schools program should be funded to allow all schools to access it.
A high-level but reasonable recommendation. In fact, the NDSS already have the National Diabetes Nursing Education Framework which would go a long way to achieving this goal. The workbook associated to the program is an outstanding resource to give this baseline understanding.
I had to look up the Diabetes in Schools program but it sounds like a great initiative.
Recommendation 15: The Committee recommends that subsidised access to Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) be further expanded. In the first instance, all access limitations in relation to patients with Type 1 diabetes should be removed. Furthermore, individuals with insulin-dependent Type 3c diabetes and patients with gestational diabetes should be made eligible for subsidised CGMs and for those with Type 2 diabetes requiring regular insulin. The Committee recommends prioritising the removal of age limitations on access to subsidised access for Type 1 diabetes patients.
This is a great recommendation. Type 3c diabetes is diabetes caused by physical damage to the pancreas. This may be as a result of an accident, surgery, or perhaps cancer. People with type 3c diabetes often fall through the cracks and have a difficult time accessing subsidy programs despite often having similar needs as people with type 1 diabetes. Expanding access to people with gestational diabetes and insulin-dependent type 2 diabetes also makes sense. This may also open up the door to extending CGM subsidies to the wider type 2 diabetes cohort in the future if evidence shows it is economically viable.
Recommendation 16: The Australian Government should explore expanding subsidised access to insulin pumps for all Australians with Type 1 diabetes. A gradual increase, such as expanding access to those aged 40 and under, would be useful as an initial step.
This is another issue I have strong thoughts on, and I was a co-author on this petition which describes why the current model is broken. I was also a signatory to the recently released Consensus Statement on Automated Insulin Delivery for Type 1 Diabetes in Australia.
A gradual increase makes sense although why it would be based on being less than 40 years of age mystifies me. As far as I know, there is no medical evidence to suggest 40 years has significance in the efficacy of pump use. For me, it would make more sense to roll it out in a manner similar to how the CGM subsidy was rolled out e.g. ((type 1 diabetes AND (21 years and under OR indigenous OR concession card holder)) OR (insulin-dependent gestational diabetes). The rest of us would access a pump in the same way as we do today and, over time, the program could expend where the evidence supports the case.
Recommendation 17: The Committee recommends that the Australian Government undertakes a review of the price and choice of insulin pumps in Australia.
I have no idea where this one is coming from. We have a pretty good choice of pumps in Australia so why fix something which is not broken? I hope this is not suggesting we have too much choice and implies we should go down a path similar to, say, New Zealand where only two pumps are funded. Choice is not a luxury; it ensures people are getting the right technology to maximise their prospect of success. Their job may mean a tubeless pump is a better choice. They may have sight impairment which means a pump which connects to a phone or which has a high-contrast screen is the best option. A wider choice ensures a broader set of people’s needs can be met.
Recommendation 18: The Committee recommends that the Australian Government, subject to a positive recommendation from the Pharmaceutical Benefits Advisory Committee, expands the eligibility criteria for Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, particularly for high-risk patients.
Yes! A great recommendation. I talked about GLP-1s and their benefits for all types of diabetes around four years ago, based on the results coming out from international conferences. These results are now filtering down to the government subsidy level and, hopefully, will soon lead to wider availability for these powerful tools although, historically, supply has been an issue.
The next generation of GLP-1s are now coming out with even more impressive results in terms of weight loss and glucose management. The most well-known is arguably Tirzepatide (Mounjaro) which is approved for people with type 2 diabetes but not type 1. Upcoming trials hope to show it is of benefit to both types of diabetes.
Recommendation 19: The Committee recommends that the Australian Government establishes mechanisms for securing supplies of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists for disadvantaged and remote communities, including Aboriginal and Torres Strait Island communities.
As mentioned in Recommendation 18, supply of GLP-1s worldwide has been an issue. Given their benefit for both weight loss and for people with diabetes, it is a good suggestion although it is not clear to me how it is to be implemented. If those of us in the cities are struggling to get supply, and the issue is worldwide, this makes access a non-starter for remote communities whose logistics challenges will only add to the problems.
Recommendation 20: The Committee recommends that the Australian Government considers expanding access to bariatric surgery within the public system for eligible patients.
For people with type 2 diabetes and obesity, bariatric surgery has an impressive remission rate of around 50-95%. In Australia, to be eligible for the surgery you must have a Body-Mass Index (BMI) of over 40, or type 2 diabetes and a BMI of over 35. The recommendation is not clear in which direction access should be expanded (lower BMI? different types of diabetes?) Also, only so many surgeries can be conducted in Australia annually and the government would need to provide significant funding to keep up with the current demand, let alone increased demand.
Recommendation 21: The Committee recommends that the Australian Government takes steps to manage diabetes research efforts through the Australian Centre for Disease Control (CDC) by coordinating with the peak bodies such as JDRF and Diabetes Australia research priorities with an emphasis on equitable access and prevention. The Committee also recommends that the Australian Government considers increased funding for Type 1 diabetes research and clinical trials.
All sensible recommendations. I assume coordination between the relevant bodies is not as efficient as it could be and thus the call for improvement. If it means better use of money to help people with diabetes, I am all for it.
Recommendation 22: The Committee recommends that the Australian Government undertakes a survey of current diabetes-related data, with a view to developing strategies for establishing new and improving current data sources and for establishing a national diabetes mellitus register within the CDC.
This is an interesting one as I thought, until recently, that Australia had pretty good data because of the NDSS diabetes database. However, when the register was first established, ‘best guesses’ were made to the type of diabetes people had, based on the information available at the time. This summary covers the history of the NDSS register and some of the problems in the quality of its data.
To give an idea of how, even today, poor data are being captured, according to the NDSS database there are literally no people with type 1 diabetes in Australia who are insulin independent. This means LADAs who, by definition, do not require insulin for at least six months after diagnosis, are lost in the system. Why is this the case? Because it is really hard to change the details in the NDSS database once a person is registered. This means all LADAs, including myself, are told to register as insulin-dependent so that access to subsidised resources is not an issue later on. In short, there is no formal recognition of LADA in Australia and certainly no data to ascertain the prevalence and characteristics of this type 1 sub-type.
Recommendation 23: The Committee recommends that the Australian Centre for Evaluation in the Department of Treasury commits to the ongoing assessment of any actions taken in respect of Committee recommendations made in this report.
This sounds more like bookkeeping than a specific diabetes-related recommendation. Accountability is good though, so I appreciate the value of it.
tl;dr
The recommendations of the inquiry are a bit of a mixed bag, driven by overly broad Terms of Reference and, arguably, pre-conceived notions on the causes of diabetes and, specifically, type 2 diabetes.
The recommendations fall into the following categories (23 is generic and has been left off):
Sugar Recommendations (3, 4)
In short, added sugar is the devil and should be treated as such (change food labelling to call out sugar has been added and tax it). No argument from me on that front but, for type 1 diabetes, total carbohydrates is the key piece of information. As long as that is not sacrificed, all good. As for a sugar tax, if in encourages more variety in sugar-free drinks, I am all for it.
Why is sugar being mentioned in an inquiry into diabetes? No idea. Sugar is not mentioned in the Terms of Reference and its inclusion will feed misconceptions about diabetes being caused by sugar eating.
Obesity Recommendations (7, 10, 20)
The obesity recommendations (design cities for exercise, screen for obesity, and make bariatric surgery more accessible) do not talk at the links between diabetes and obesity, as outlined in the Terms of Reference and tenuously relate to “the causes of obesity and the evidence-base in the prevention, diagnosis and management of obesity”. I would argue they miss this mark given there is limited evidence that city design improves obesity rates. As for the final two recommendations, without investment in what happens after a positive screening and in bariatric services, all we are doing is creating demand for a system which is not set up to serve it.
General Health Recommendations (2, 5, 6)
In short, review dietary guidelines, regulate the advertising of unhealthy food to children, and ensure access to healthy food. All great ideas, and all as relevant to diabetes as they are to many other diseases where diet is considered a risk factor. Should they be in the recommendations for an inquiry into diabetes? Is there evidence that any of these measures will impact diabetes in the Australian population? Do they align to the specified Terms of Reference? No.
Diabetes Recommendations (1, 8, 9, 11-19, 21, 22)
The remaining two thirds of the recommendations actually relate to diabetes, which is good. Economic rigour around the cost of diabetes is a great idea (1) and provides a foundation for smart, economically responsible decisions. Screening for diabetes (I have no idea why they focus on type 2 diabetes here) and increasing overall awareness to enable ‘self-screening’ (8, 9, 11) makes a lot of sense. Catching diabetes early in all of its forms improves outcomes for the individual and the country.
Improved access to health care professionals (12, 13) for all Australians is a good idea but the shortage of these professionals is not considered in the recommendations and risks straining an already strained system further.
The call for improved education of health care professionals in their knowledge of diabetes (14) is a great idea. Many people with diabetes (especially people with type 1 diabetes) actively avoid engaging with the health system because they know they will need to educate the HCP themselves and, often, their knowledge and experience will not be respected and ignored for a lecture received back in medical school decades earlier. Improved education is a tide which will raise all boats and improve the system for all.
Improved and subsidised access to proven medications and technologies (15, 16, 18, 19) is a great idea although I am concerned about the suggestion to review the choice of pumps (17) unless this is aimed at getting the most recent pumps into the country as Australia is a version behind in many CGM and pump systems. The suggestion to use a cut-off of 40 years of age for pump subsidy confounds me and is misaligned to previous Australian subsidy schemes and pump subsidy schemes being rolled out internationally.
Improved research funding administration and access to data (21, 22), as with Recommendation 1, will only improve the decisions made in the future. We can only set our direction when we know where we are, where we are wanting to get to and the means we have to get there, and while many of the recommendations make good guesses to the direction we should head, Recommendations 1, 21, and 22 enable a foundation for much smarter navigation.
Conclusions
There are some good ideas here but there are also missed opportunities and half-solutions. Screening for different diabetes types and for obesity is well and good but what then? The emergence of immune intervention treatments for type 1 diabetes e.g. Teplizumab is also a missed opportunity and a great solution to the question of screening next steps. The lack of health care professionals to service the diabetes community is also absent from the recommendations despite calls to increase demand.
I look forward to seeing how these recommendations are implemented and hope, the ones which are truly focussed on diabetes get the attention they deserve. Diabetes is a costly disease for both the individual and the country so smart, evidence-based decisions, will make a big difference.